Diaphragm Wall / Cap Stake
Diaphragm wall
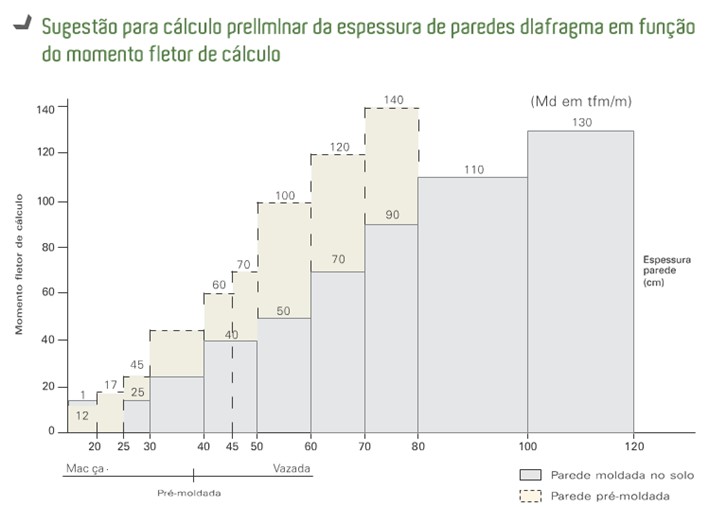
The cast-in-place diaphragm wall has a variable thickness of 30cm to 120cm and can reach depths exceeding 50m. The excavation is performed using a clamshell and stabilizing fluid. The diaphragm panels are constructed from the ground surface in adjacent panels with a width of 2.50m or 3.20m, and their continuity is ensured by the use of a tube or joint plate, which is installed before the concrete placement and removed shortly after the concrete begins to harden.
The plastic diaphragm wall forms a watertight barrier of "coulis" (a mixture of cement + bentonite + water) with proportions that vary depending on the desired permeability. This barrier prevents the flow of water or any other fluid.
The precast diaphragm wall is made up of precast panels that may or may not be concreted in situ. To ensure the watertightness of the joints, the excavated trench, filled with stabilizing fluid, is filled with "coulis" before placing the panels.
Cap Stake
It consists of drilling into the ground and then filling the hole with concrete. During the concreting process, a steel bar is inserted into the hole, creating a reinforced concrete pile.
In addition, cap piles can be designed to accommodate different types of loads and ground conditions, making them a versatile solution for a variety of construction projects.
Its application requires specialized technical knowledge to determine the correct type of piles, the proper spacing and other design parameters in order to guarantee the safety and long-term stability of the constructed structure.
Therefore, cap piles play a crucial role in civil engineering, allowing the safe and durable construction of buildings and infrastructure in different geotechnical conditions.